Table of Contents
Depending on your position in betterment, there are many types of procedures to help limit the impact of your investment on your tax bill. Let’s demolish these powerful strategies.
We know that the medley of account types can make it challenging for you to decide which account to contribute or withdraw from any time.
Let’s get the right dive to get another understanding:
- What are accounts available and why you can choose them
- Benefits of getting dividends
- Powerful tax-sensitive features
How is tax imposed on various investment accounts?
Taxable account
Taxable investment accounts are usually the easiest to establish and have minimal restrictions.
Although you can easily contribute and withdraw from the account at any time, but there are trading. A taxable account is funded with taxable dollar, and any capital gains that you receive by selling property, as well as any dividend you receive, are taxable on an annual basis.
While there is no postponement of income in a retirement scheme, only taxable accounts have special tax benefits such as long -term profit, qualified dividends and municipal bond income at low rates on income.
Main idea
- You would like the option to withdraw with IRS punishment at any time.
- You already contributed the maximum amount to all tax-deprived retirement accounts.
Traditional account
Traditional accounts include traditional IRA, traditional 401 (K) S, traditional 403 (B) S, traditional 457 government schemes and traditional Thrift Saving Plan (TSP).
Traditional investment accounts for retirement are usually funded with pre-tax dollars. The investment income received is postponed until the time of distribution from the scheme. Assuming that all contributions have been funded with pre-tax dollars, distribution is perfectly taxable as normal income. For investors under the age of 59.5, until no discount applies, an additional 10% initial withdrawal can be fined.
Main idea
- You hope that your tax rate will now be low in retirement.
- You recognize and accept the possibility of an initial return punishment.
Roth accounts
This includes Roth Ira, Roth 401 (K) S, Roth 403 (B) S, Roth 457 Government Schemes, and Roth Thrift Saving Plan (TSP).
Roth type investment accounts for retirement are always funded with tax-bey dollars. Eligible distribution is tax-free. For investors under the age of 59.5, earnings can be an additional 10% initial withdrawal penalty on earnings and until the discount applies.
Main idea
- You hope that your tax rate will be higher in retirement, as it is now.
- You hope that your revised adjusted gross income (AGI) will be below $ 140K (or jointly $ 208K filing).
- You want the option to withdraw contribution without doing tax.
- You recognize the possibility of fine on earnings.
Beyond account types of decisions, we use your dividend to keep your tax effect as low as possible.
Four methods better help you limit your tax effects
We use any additional cash to regenerate our portfolio
When your account receives a cash – whether it is through dividend or deposit – we automatically recognize how to use money to help each asset class back your target load.
Dividend is part of a company’s earnings. Not all companies pay dividends, but as a better investor, you almost always receive something because your money is invested in thousands of companies in the world.
Your dividends are an essential component in our tax-skilled rebelling process. When you receive dividends in your betterment account, you are not only earning money as an investor-your portfolio is also getting a quick micro-restability, which aims to help keep your tax bill down at the end of the year.
And, when market movements cause the actual allocation of your portfolio to remove from your target allocation, we automatically use any upcoming dividend or deposit to buy more shares of our portfolio’s leggings part.
This helps the portfolio back into its targeted asset allocation without selling shares. It is a sophisticated financial planning technique that is traditionally available for large accounts, but makes our automation possible to do it with any size account.
Performing S&P 500 with dividend regenerated
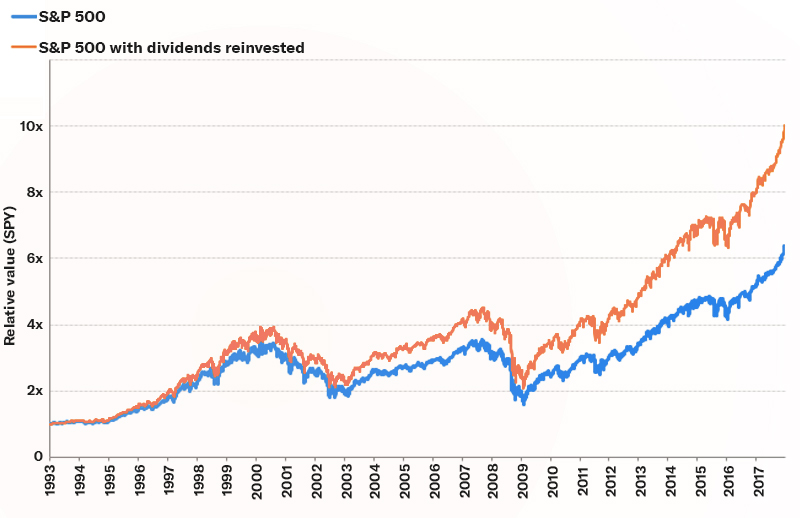
Source: BloombergPerformance is provided for illustration purposes to represent wide market returns [asset classes] It cannot be used in all better portfolio. [asset class] The performance is not responsible for any real better portfolio nor does it reflect any specific better performance. For example, it is not a network of any management fee. The performance of specific funds used for each asset class in better portfolio will vary from the performance of the wide market index returns reflected here. Past performance is not indicative of future results. You cannot invest directly in the index. The material is for educational purposes and is not intended to take as advice or recommendation for any specific investment product or strategy.
We “crop” investment deficit
Tax loss harvesting can reduce your tax bill, while you can reduce the “harvesting” investment deficit for tax reporting purposes while investing completely.
The price that has increased when selling an investment, you will pay taxes on profit, known as capital gains tax. Fortunately, the tax code considers your profit and disadvantage in all your investments while assessing the capital profit tax, which means that any disadvantage (also in other investments) will reduce your profit and your tax bill.
In fact, if there is profit due to deficit in a tax year, you can completely eliminate your capital gain bill. The remaining of any loss can be used to reduce your taxable income by $ 3,000. Finally, any losses not used in the current tax year can be taken indefinitely to reduce capital gains and taxable income over the years.
So how do you do it?
When an investment falls below its initial value – there is something that is likely to be the best investment at a point during your investment horizon – you sell that investment to realize losses for tax objectives and to buy related investments to maintain your market risk.
Ideally, you will buy the same investment that you have just sold. After all, you still feel that this is a good investment. However, IRS rules prevent you from identifying tax losses if you buy uniform investment within 30 days of sales. Therefore, to maintain your overall investment risk, you buy a related but separate investment. Think about selling coke stock and then buying Pepsi stock.
Overall, tax loss harvesting can help reduce your tax bill by recognizing the loss while maintaining your overall market risk. In the better, you only have to turn on tax harvesting tax harvesting in your account.
We use asset location for your benefit
Asset location is a strategy where you keep your most tax-capable investment (usually bond) in tax-skilled accounts (IRA or 401K) while maintaining your overall portfolio mix.
For example, an investor can save for retirement in an IRA and taxable account and has a overall portfolio mixture of 60% shares and 40% bonds. Instead of placing a 60/40 mixture in both accounts, an investor using a property location strategy will put a tax-worth bond in the IRA and put more tax-skilled stock in a taxable account.
In doing so, interest income from bonds – which is generally considered as simple income and is preserved by taxes in IRA subject to a high tax rate. Meanwhile, in the taxable account, the dividend qualified from shares is levied at low rates, capital profit tax rates rather than general income tax rates. The entire portfolio still maintains a 60/40 mixture, but the underlying accounts have transferred the property between each other to reduce the tax burden of the portfolio.
We use ETF instead of mutual funds
Have you ever paid a capital gain tax on a mutual fund which was below in the year? This disappointing situation occurs when the fund sells investment inside the fund for a profit, even if the overall fund is lost. The IRS rule gives the mandate that the tax on these benefits is passed through the final investor, you.
While the same rule applies to the exchange of traded funds (ETFs), the ETF fund structure makes such tax bills very little. In most cases, you can find ETFs with investment strategies that are similar or similar to a mutual fund, often with low fees.


